Selection sort is a sorting algorithm that selects the smallest element from an unsorted list in each iteration and places that element at the beginning of the unsorted list.
Working of Selection Sort
- Set the first element as
minimum.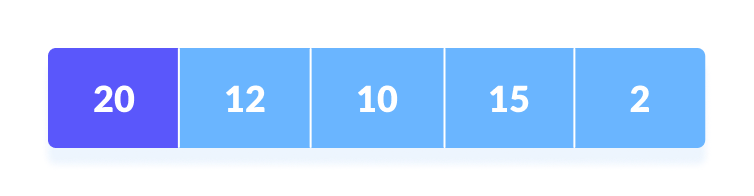
Select first element as minimum - Compare
minimumwith the second element. If the second element is smaller thanminimum, assign the second element asminimum.
Compareminimumwith the third element. Again, if the third element is smaller, then assignminimumto the third element otherwise do nothing. The process goes on until the last element.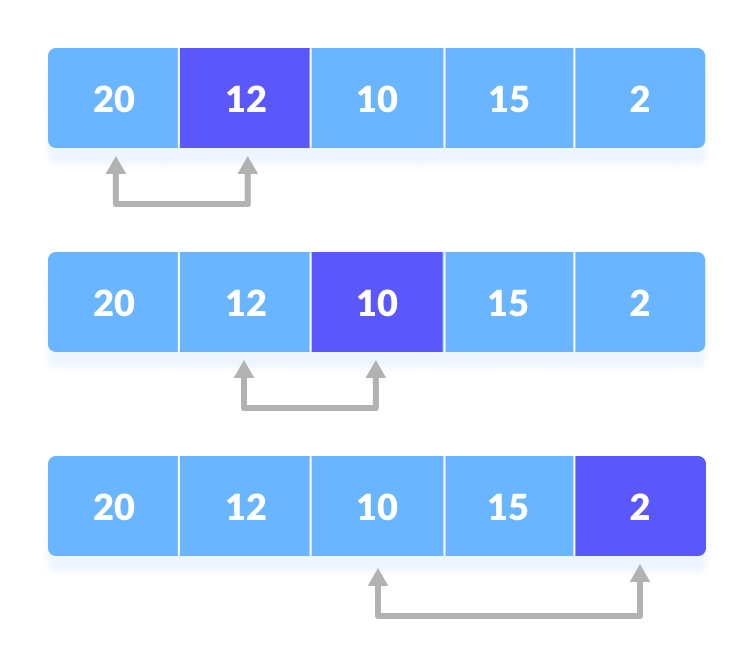
Compare minimum with the remaining elements - After each iteration,
minimumis placed in the front of the unsorted list.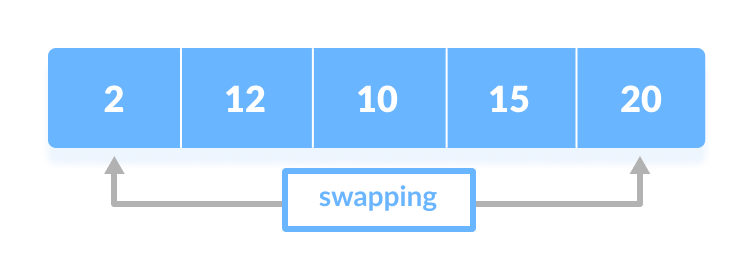
Swap the first with minimum - For each iteration, indexing starts from the first unsorted element. Step 1 to 3 are repeated until all the elements are placed at their correct positions.
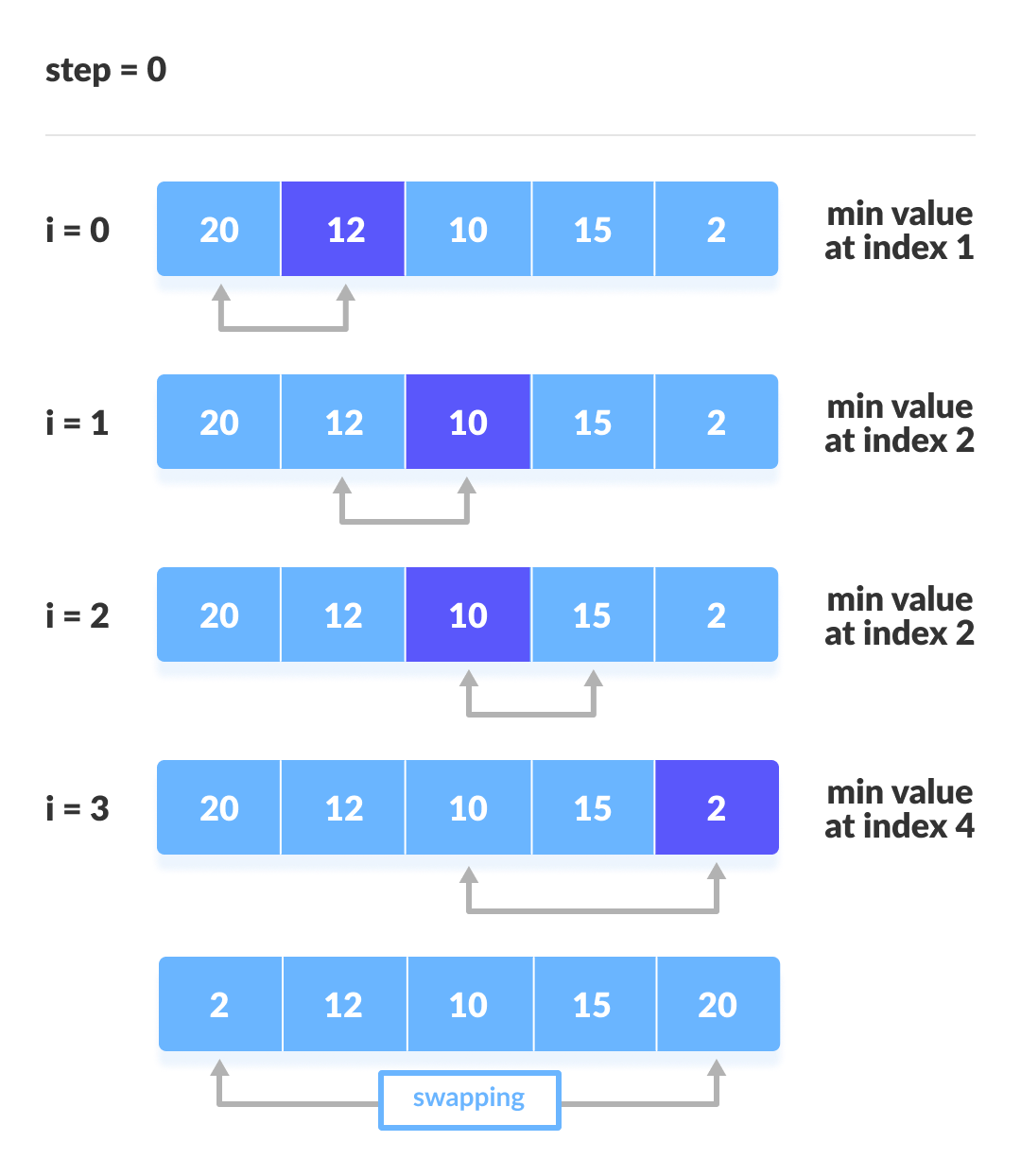
The first iteration 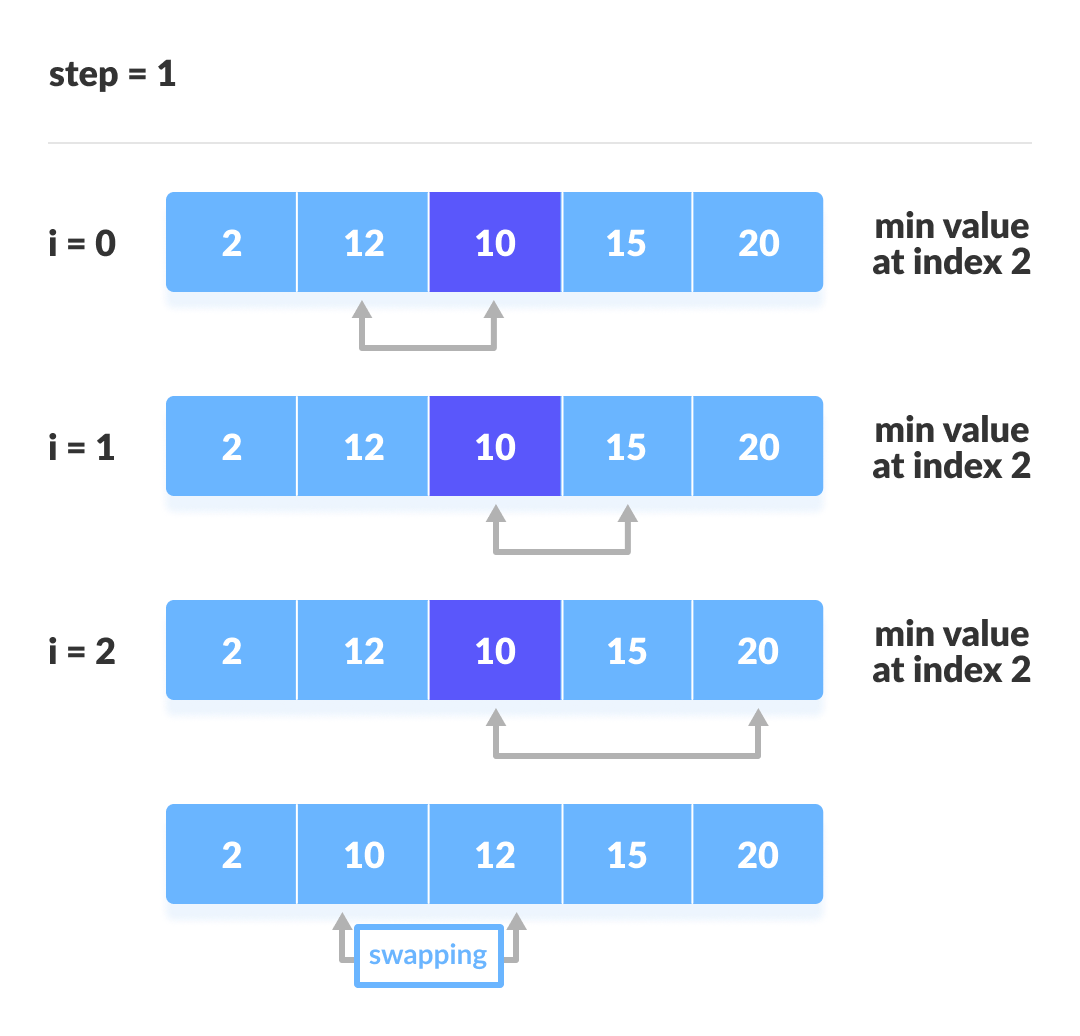
The second iteration 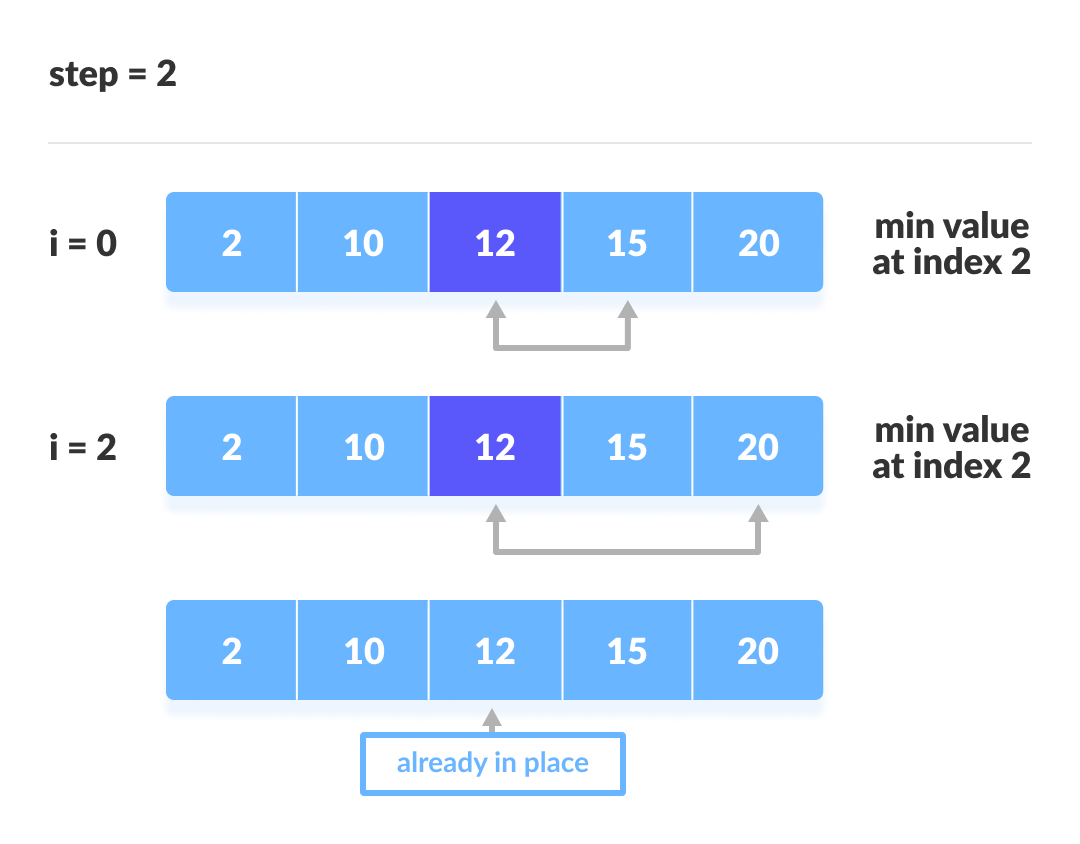
The third iteration 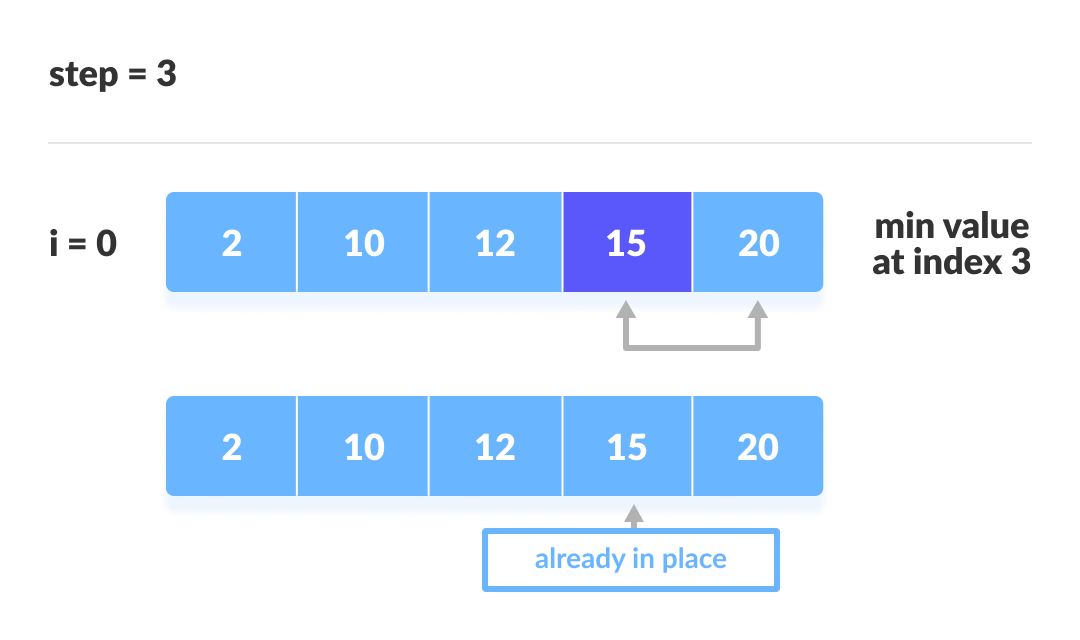
The fourth iteration
Selection Sort Algorithm
selectionSort(array, size)
for i from 0 to size - 1 do
set i as the index of the current minimum
for j from i + 1 to size - 1 do
if array[j] < array[current minimum]
set j as the new current minimum index
if current minimum is not i
swap array[i] with array[current minimum]
end selectionSortSelection Sort Code in Python, Java, and C/C++
# Selection sort in Python
def selectionSort(array, size):
for step in range(size):
min_idx = step
for i in range(step + 1, size):
# to sort in descending order, change > to < in this line
# select the minimum element in each loop
if array[i] < array[min_idx]:
min_idx = i
# put min at the correct position
(array[step], array[min_idx]) = (array[min_idx], array[step])
data = [-2, 45, 0, 11, -9]
size = len(data)
selectionSort(data, size)
print('Sorted Array in Ascending Order:')
print(data)
// Selection sort in Java
import java.util.Arrays;
class SelectionSort {
void selectionSort(int array[]) {
int size = array.length;
for (int step = 0; step < size - 1; step++) {
int min_idx = step;
for (int i = step + 1; i < size; i++) {
// To sort in descending order, change > to < in this line.
// Select the minimum element in each loop.
if (array[i] < array[min_idx]) {
min_idx = i;
}
}
// put min at the correct position
int temp = array[step];
array[step] = array[min_idx];
array[min_idx] = temp;
}
}
// driver code
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] data = { 20, 12, 10, 15, 2 };
SelectionSort ss = new SelectionSort();
ss.selectionSort(data);
System.out.println("Sorted Array in Ascending Order: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
}
}
// Selection sort in C
#include <stdio.h>
// function to swap the the position of two elements
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
void selectionSort(int array[], int size) {
for (int step = 0; step < size - 1; step++) {
int min_idx = step;
for (int i = step + 1; i < size; i++) {
// To sort in descending order, change > to < in this line.
// Select the minimum element in each loop.
if (array[i] < array[min_idx])
min_idx = i;
}
// put min at the correct position
swap(&array[min_idx], &array[step]);
}
}
// function to print an array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// driver code
int main() {
int data[] = {20, 12, 10, 15, 2};
int size = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
selectionSort(data, size);
printf("Sorted array in Acsending Order:\n");
printArray(data, size);
}
// Selection sort in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// function to swap the the position of two elements
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
// function to print an array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cout << array[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void selectionSort(int array[], int size) {
for (int step = 0; step < size - 1; step++) {
int min_idx = step;
for (int i = step + 1; i < size; i++) {
// To sort in descending order, change > to < in this line.
// Select the minimum element in each loop.
if (array[i] < array[min_idx])
min_idx = i;
}
// put min at the correct position
swap(&array[min_idx], &array[step]);
}
}
// driver code
int main() {
int data[] = {20, 12, 10, 15, 2};
int size = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
selectionSort(data, size);
cout << "Sorted array in Acsending Order:\n";
printArray(data, size);
}
Selection Sort Complexity
| Time Complexity | |
|---|---|
| Best | O(n2) |
| Worst | O(n2) |
| Average | O(n2) |
| Space Complexity | O(1) |
| Stability | No |
| Cycle | Number of Comparison |
|---|---|
| 1st | (n-1) |
| 2nd | (n-2) |
| 3rd | (n-3) |
| ... | ... |
| last | 1 |
Number of comparisons: (n - 1) + (n - 2) + (n - 3) + ..... + 1 = n(n - 1) / 2 nearly equals to n2.
Complexity = O(n2)
Also, we can analyze the complexity by simply observing the number of loops. There are 2 loops so the complexity is n*n = n2.
Time Complexities:
- Worst Case Complexity:
O(n2)
If we want to sort in ascending order and the array is in descending order then, the worst case occurs. - Best Case Complexity:
O(n2)
It occurs when the array is already sorted - Average Case Complexity:
O(n2)
It occurs when the elements of the array are in jumbled order (neither ascending nor descending).
The time complexity of the selection sort is the same in all cases. At every step, you have to find the minimum element and put it in the right place. The minimum element is not known until the end of the array is not reached.
Space Complexity:
Space complexity is O(1) because an extra variable min_idx is used.
Selection Sort Applications
The selection sort is used when
- a small list is to be sorted
- cost of swapping does not matter
- checking of all the elements is compulsory
- cost of writing to a memory matters like in flash memory (number of writes/swaps is
O(n)as compared toO(n2)of bubble sort)