It differs from the minimum spanning tree because the shortest distance between two vertices might not include all the vertices of the graph.
How Dijkstra's Algorithm works
Dijkstra's Algorithm works on the basis that any subpath B -> D of the shortest path A -> D between vertices A and D is also the shortest path between vertices B and D.
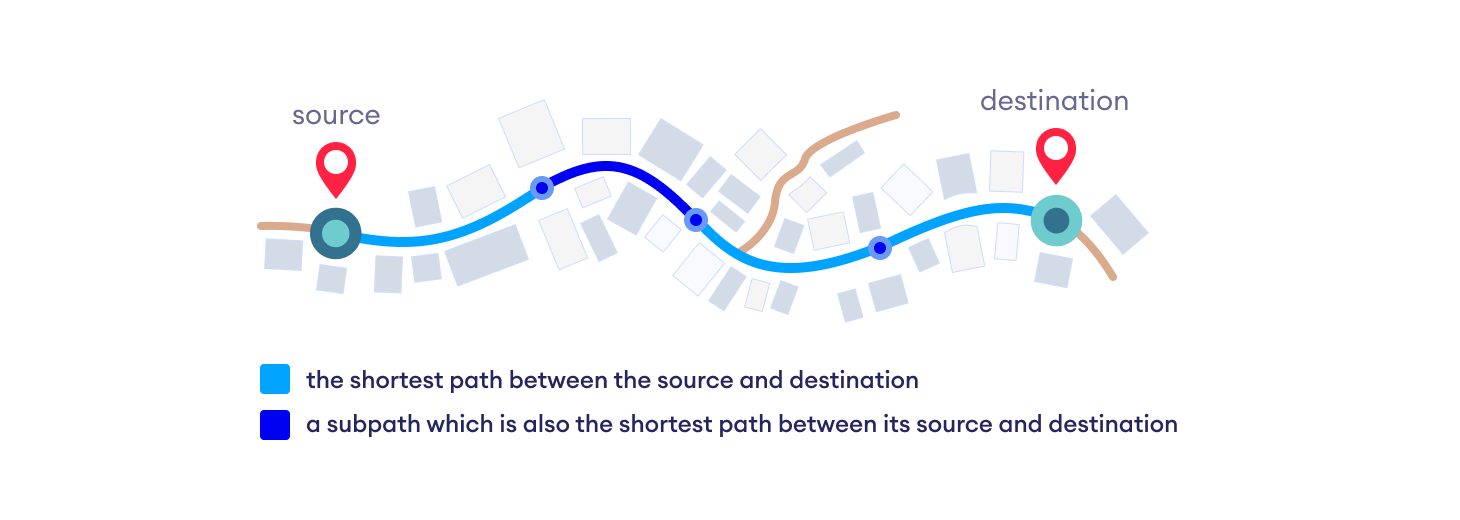
Djikstra used this property in the opposite direction i.e we overestimate the distance of each vertex from the starting vertex. Then we visit each node and its neighbors to find the shortest subpath to those neighbors.
The algorithm uses a greedy approach in the sense that we find the next best solution hoping that the end result is the best solution for the whole problem.
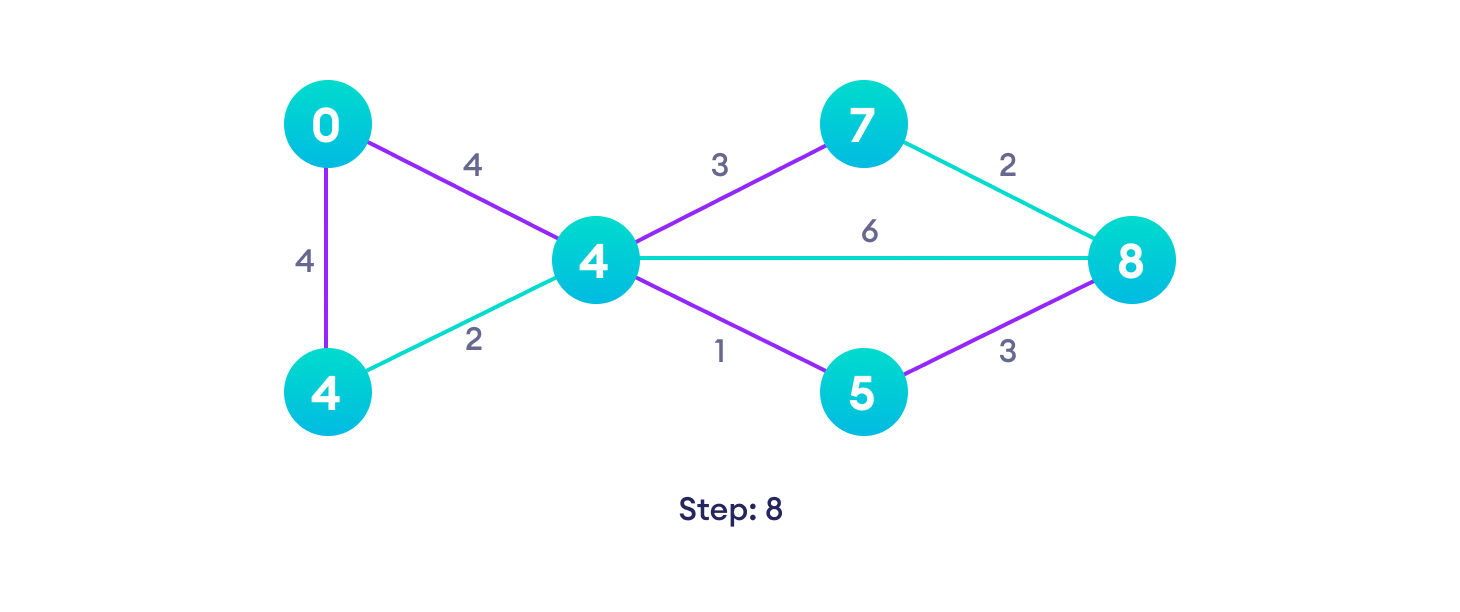
Example of Dijkstra's algorithm
It is easier to start with an example and then think about the algorithm.
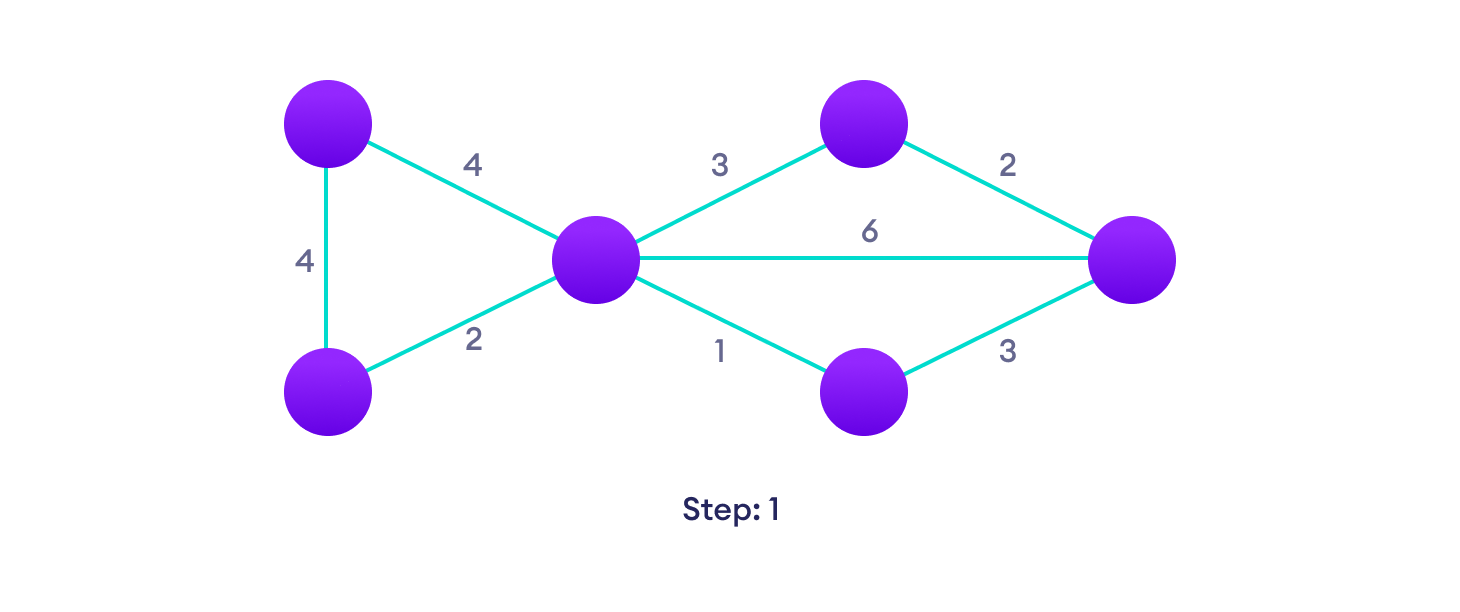
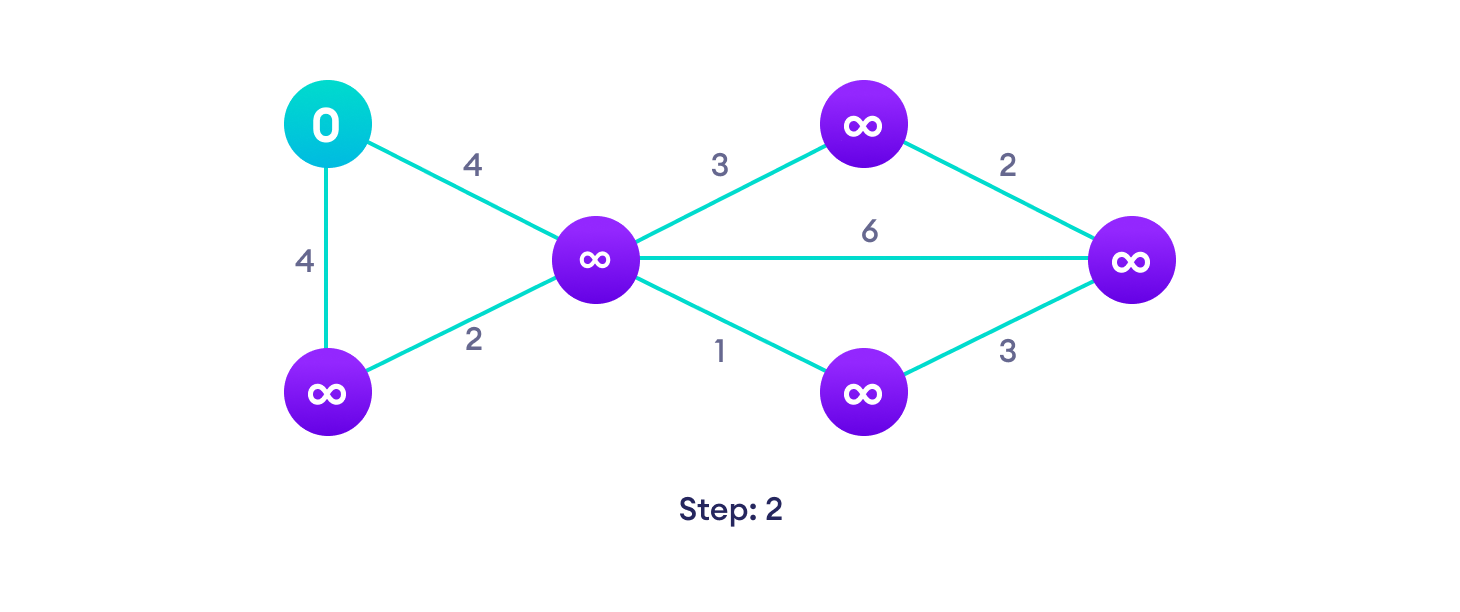
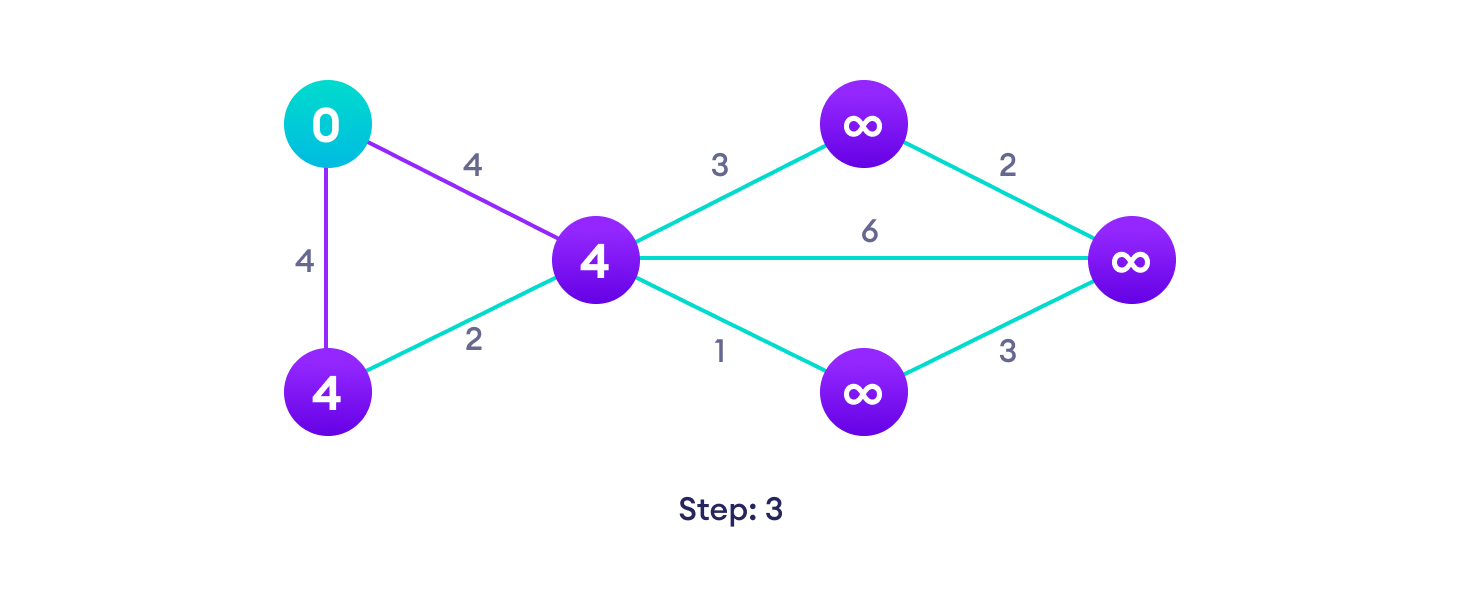
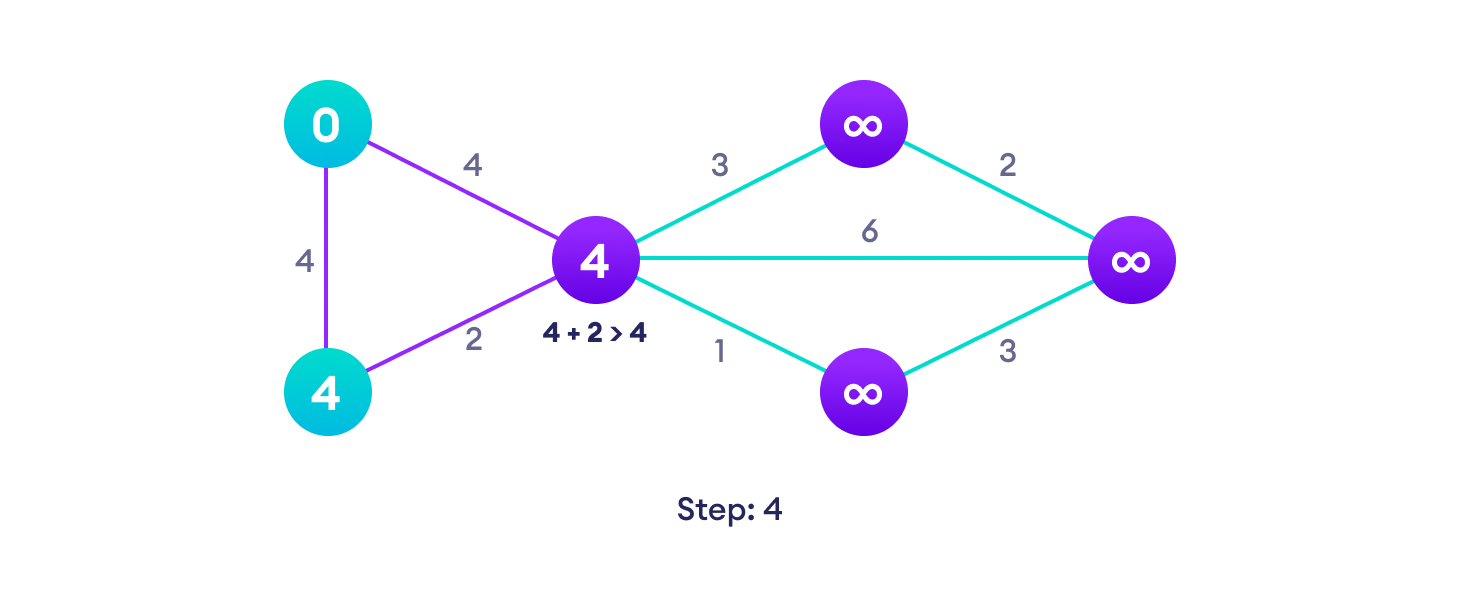
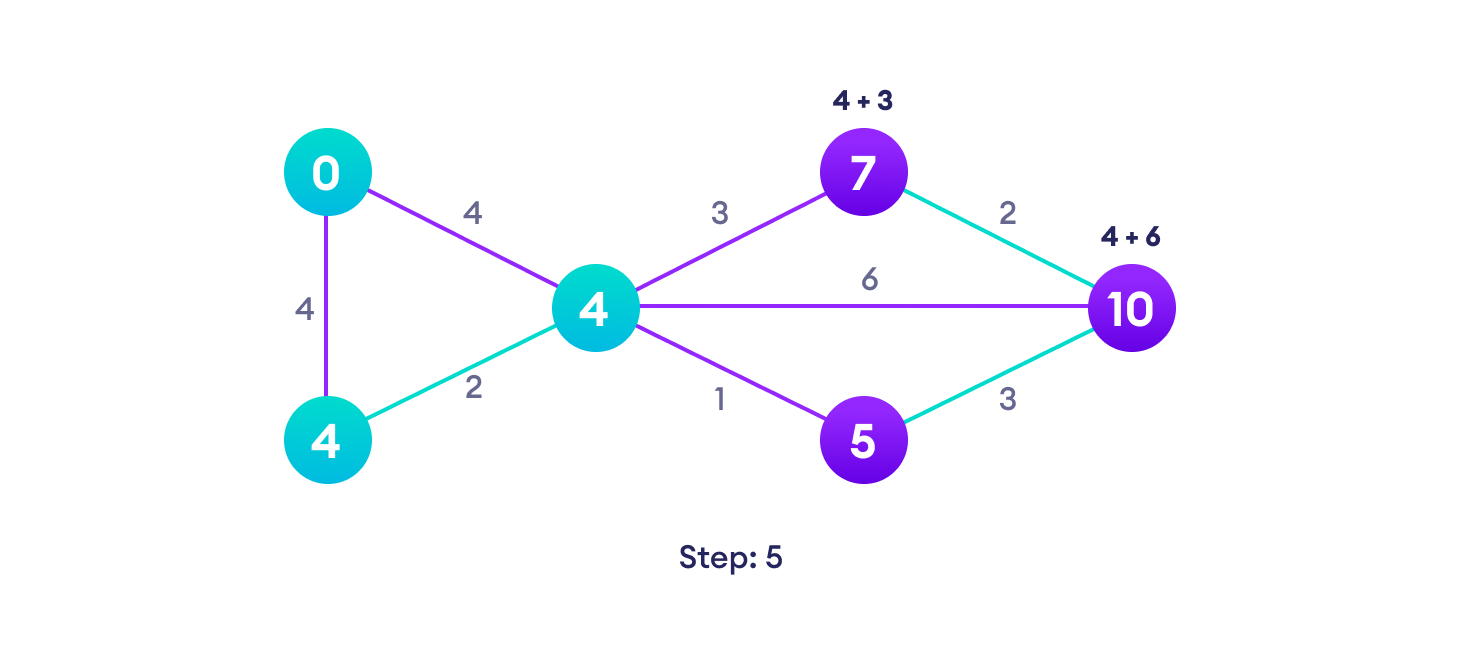
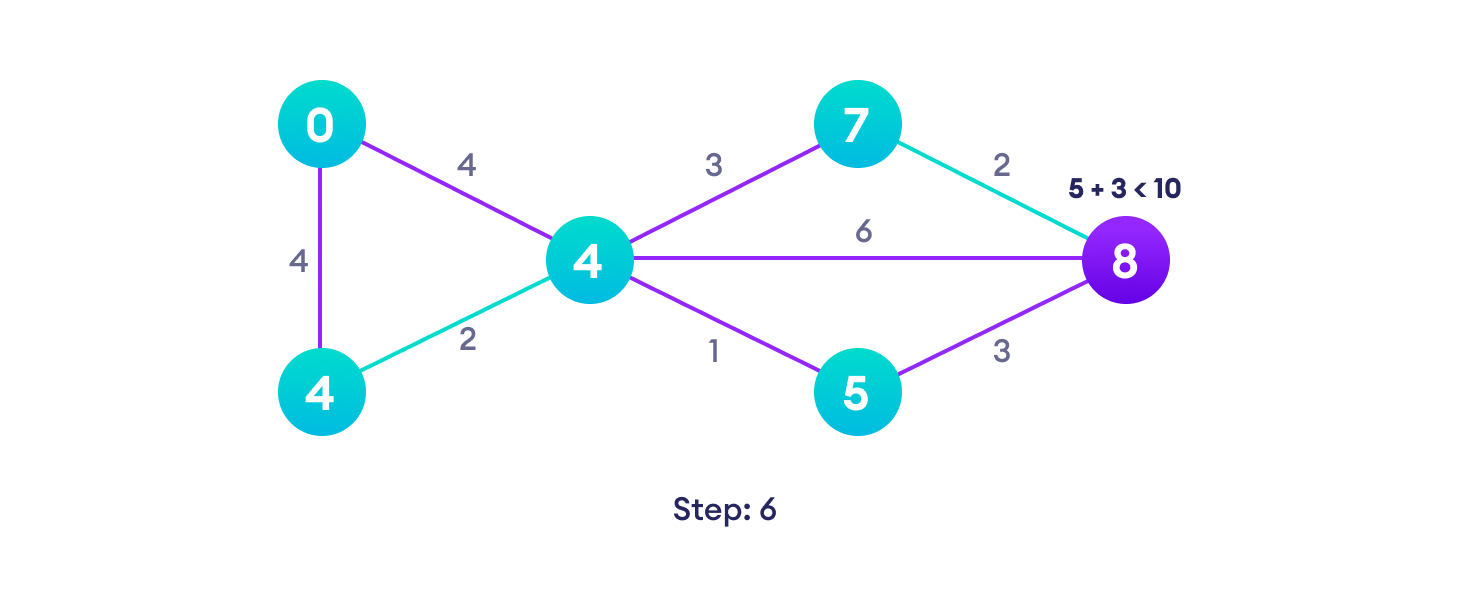
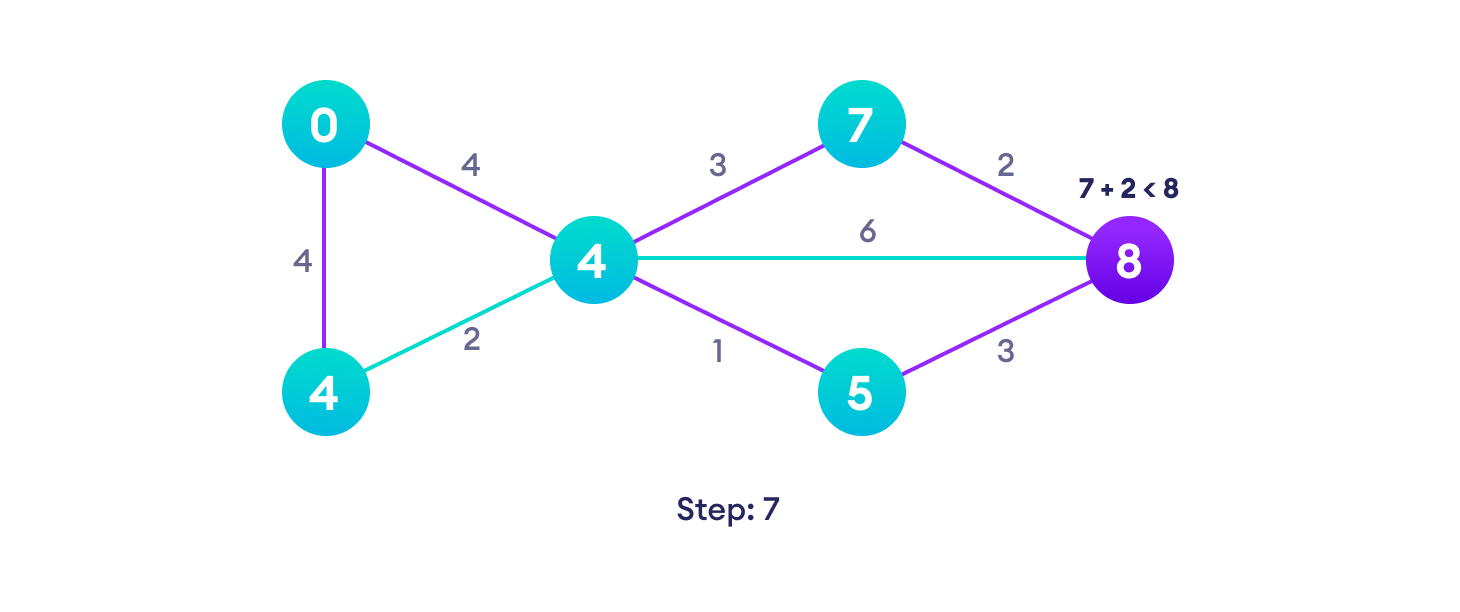
Djikstra's algorithm pseudocode
We need to maintain the path distance of every vertex. We can store that in an array of size v, where v is the number of vertices.
We also want to be able to get the shortest path, not only know the length of the shortest path. For this, we map each vertex to the vertex that last updated its path length.
Once the algorithm is over, we can backtrack from the destination vertex to the source vertex to find the path.
A minimum priority queue can be used to efficiently receive the vertex with least path distance.
function dijkstra(G, S)
for each vertex V in G
distance[V] <- infinite
previous[V] <- NULL
If V != S, add V to Priority Queue Q
distance[S] <- 0
while Q IS NOT EMPTY
U <- Extract MIN from Q
for each unvisited neighbour V of U
tempDistance <- distance[U] + edge_weight(U, V)
if tempDistance < distance[V]
distance[V] <- tempDistance
previous[V] <- U
return distance[], previous[]
Code for Dijkstra's Algorithm
The implementation of Dijkstra's Algorithm in Python, Java, C and C++ is given below. The complexity of the code can be improved, but the abstractions are convenient to relate the code with the algorithm.
# Dijkstra's Algorithm in Python
import sys
# Providing the graph
vertices = [[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0]]
edges = [[0, 0, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 3, 0],
[1, 2, 0, 1, 3, 0, 0],
[2, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 3, 0, 0, 2, 0],
[0, 3, 0, 0, 2, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0]]
# Find which vertex is to be visited next
def to_be_visited():
global visited_and_distance
v = -10
for index in range(num_of_vertices):
if visited_and_distance[index][0] == 0 \
and (v < 0 or visited_and_distance[index][1] <=
visited_and_distance[v][1]):
v = index
return v
num_of_vertices = len(vertices[0])
visited_and_distance = [[0, 0]]
for i in range(num_of_vertices-1):
visited_and_distance.append([0, sys.maxsize])
for vertex in range(num_of_vertices):
# Find next vertex to be visited
to_visit = to_be_visited()
for neighbor_index in range(num_of_vertices):
# Updating new distances
if vertices[to_visit][neighbor_index] == 1 and \
visited_and_distance[neighbor_index][0] == 0:
new_distance = visited_and_distance[to_visit][1] \
+ edges[to_visit][neighbor_index]
if visited_and_distance[neighbor_index][1] > new_distance:
visited_and_distance[neighbor_index][1] = new_distance
visited_and_distance[to_visit][0] = 1
i = 0
# Printing the distance
for distance in visited_and_distance:
print("Distance of ", chr(ord('a') + i),
" from source vertex: ", distance[1])
i = i + 1
// Dijkstra's Algorithm in Java
public class Dijkstra {
public static void dijkstra(int[][] graph, int source) {
int count = graph.length;
boolean[] visitedVertex = new boolean[count];
int[] distance = new int[count];
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
visitedVertex[i] = false;
distance[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
// Distance of self loop is zero
distance[source] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
// Update the distance between neighbouring vertex and source vertex
int u = findMinDistance(distance, visitedVertex);
visitedVertex[u] = true;
// Update all the neighbouring vertex distances
for (int v = 0; v < count; v++) {
if (!visitedVertex[v] && graph[u][v] != 0 && (distance[u] + graph[u][v] < distance[v])) {
distance[v] = distance[u] + graph[u][v];
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < distance.length; i++) {
System.out.println(String.format("Distance from %s to %s is %s", source, i, distance[i]));
}
}
// Finding the minimum distance
private static int findMinDistance(int[] distance, boolean[] visitedVertex) {
int minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int minDistanceVertex = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < distance.length; i++) {
if (!visitedVertex[i] && distance[i] < minDistance) {
minDistance = distance[i];
minDistanceVertex = i;
}
}
return minDistanceVertex;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int graph[][] = new int[][] { { 0, 0, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 3, 0 }, { 1, 2, 0, 1, 3, 0, 0 },
{ 2, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1 }, { 0, 0, 3, 0, 0, 2, 0 }, { 0, 3, 0, 0, 2, 0, 1 }, { 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 } };
Dijkstra T = new Dijkstra();
T.dijkstra(graph, 0);
}
}
// Dijkstra's Algorithm in C
#include <stdio.h>
#define INFINITY 9999
#define MAX 10
void Dijkstra(int Graph[MAX][MAX], int n, int start);
void Dijkstra(int Graph[MAX][MAX], int n, int start) {
int cost[MAX][MAX], distance[MAX], pred[MAX];
int visited[MAX], count, mindistance, nextnode, i, j;
// Creating cost matrix
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
if (Graph[i][j] == 0)
cost[i][j] = INFINITY;
else
cost[i][j] = Graph[i][j];
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
distance[i] = cost[start][i];
pred[i] = start;
visited[i] = 0;
}
distance[start] = 0;
visited[start] = 1;
count = 1;
while (count < n - 1) {
mindistance = INFINITY;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (distance[i] < mindistance && !visited[i]) {
mindistance = distance[i];
nextnode = i;
}
visited[nextnode] = 1;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (!visited[i])
if (mindistance + cost[nextnode][i] < distance[i]) {
distance[i] = mindistance + cost[nextnode][i];
pred[i] = nextnode;
}
count++;
}
// Printing the distance
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (i != start) {
printf("\nDistance from source to %d: %d", i, distance[i]);
}
}
int main() {
int Graph[MAX][MAX], i, j, n, u;
n = 7;
Graph[0][0] = 0;
Graph[0][1] = 0;
Graph[0][2] = 1;
Graph[0][3] = 2;
Graph[0][4] = 0;
Graph[0][5] = 0;
Graph[0][6] = 0;
Graph[1][0] = 0;
Graph[1][1] = 0;
Graph[1][2] = 2;
Graph[1][3] = 0;
Graph[1][4] = 0;
Graph[1][5] = 3;
Graph[1][6] = 0;
Graph[2][0] = 1;
Graph[2][1] = 2;
Graph[2][2] = 0;
Graph[2][3] = 1;
Graph[2][4] = 3;
Graph[2][5] = 0;
Graph[2][6] = 0;
Graph[3][0] = 2;
Graph[3][1] = 0;
Graph[3][2] = 1;
Graph[3][3] = 0;
Graph[3][4] = 0;
Graph[3][5] = 0;
Graph[3][6] = 1;
Graph[4][0] = 0;
Graph[4][1] = 0;
Graph[4][2] = 3;
Graph[4][3] = 0;
Graph[4][4] = 0;
Graph[4][5] = 2;
Graph[4][6] = 0;
Graph[5][0] = 0;
Graph[5][1] = 3;
Graph[5][2] = 0;
Graph[5][3] = 0;
Graph[5][4] = 2;
Graph[5][5] = 0;
Graph[5][6] = 1;
Graph[6][0] = 0;
Graph[6][1] = 0;
Graph[6][2] = 0;
Graph[6][3] = 1;
Graph[6][4] = 0;
Graph[6][5] = 1;
Graph[6][6] = 0;
u = 0;
Dijkstra(Graph, n, u);
return 0;
}
// Dijkstra's Algorithm in C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#define INT_MAX 10000000
using namespace std;
void DijkstrasTest();
int main() {
DijkstrasTest();
return 0;
}
class Node;
class Edge;
void Dijkstras();
vector<Node*>* AdjacentRemainingNodes(Node* node);
Node* ExtractSmallest(vector<Node*>& nodes);
int Distance(Node* node1, Node* node2);
bool Contains(vector<Node*>& nodes, Node* node);
void PrintShortestRouteTo(Node* destination);
vector<Node*> nodes;
vector<Edge*> edges;
class Node {
public:
Node(char id)
: id(id), previous(NULL), distanceFromStart(INT_MAX) {
nodes.push_back(this);
}
public:
char id;
Node* previous;
int distanceFromStart;
};
class Edge {
public:
Edge(Node* node1, Node* node2, int distance)
: node1(node1), node2(node2), distance(distance) {
edges.push_back(this);
}
bool Connects(Node* node1, Node* node2) {
return (
(node1 == this->node1 &&
node2 == this->node2) ||
(node1 == this->node2 &&
node2 == this->node1));
}
public:
Node* node1;
Node* node2;
int distance;
};
///////////////////
void DijkstrasTest() {
Node* a = new Node('a');
Node* b = new Node('b');
Node* c = new Node('c');
Node* d = new Node('d');
Node* e = new Node('e');
Node* f = new Node('f');
Node* g = new Node('g');
Edge* e1 = new Edge(a, c, 1);
Edge* e2 = new Edge(a, d, 2);
Edge* e3 = new Edge(b, c, 2);
Edge* e4 = new Edge(c, d, 1);
Edge* e5 = new Edge(b, f, 3);
Edge* e6 = new Edge(c, e, 3);
Edge* e7 = new Edge(e, f, 2);
Edge* e8 = new Edge(d, g, 1);
Edge* e9 = new Edge(g, f, 1);
a->distanceFromStart = 0; // set start node
Dijkstras();
PrintShortestRouteTo(f);
}
///////////////////
void Dijkstras() {
while (nodes.size() > 0) {
Node* smallest = ExtractSmallest(nodes);
vector<Node*>* adjacentNodes =
AdjacentRemainingNodes(smallest);
const int size = adjacentNodes->size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
Node* adjacent = adjacentNodes->at(i);
int distance = Distance(smallest, adjacent) +
smallest->distanceFromStart;
if (distance < adjacent->distanceFromStart) {
adjacent->distanceFromStart = distance;
adjacent->previous = smallest;
}
}
delete adjacentNodes;
}
}
// Find the node with the smallest distance,
// remove it, and return it.
Node* ExtractSmallest(vector<Node*>& nodes) {
int size = nodes.size();
if (size == 0) return NULL;
int smallestPosition = 0;
Node* smallest = nodes.at(0);
for (int i = 1; i < size; ++i) {
Node* current = nodes.at(i);
if (current->distanceFromStart <
smallest->distanceFromStart) {
smallest = current;
smallestPosition = i;
}
}
nodes.erase(nodes.begin() + smallestPosition);
return smallest;
}
// Return all nodes adjacent to 'node' which are still
// in the 'nodes' collection.
vector<Node*>* AdjacentRemainingNodes(Node* node) {
vector<Node*>* adjacentNodes = new vector<Node*>();
const int size = edges.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
Edge* edge = edges.at(i);
Node* adjacent = NULL;
if (edge->node1 == node) {
adjacent = edge->node2;
} else if (edge->node2 == node) {
adjacent = edge->node1;
}
if (adjacent && Contains(nodes, adjacent)) {
adjacentNodes->push_back(adjacent);
}
}
return adjacentNodes;
}
// Return distance between two connected nodes
int Distance(Node* node1, Node* node2) {
const int size = edges.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
Edge* edge = edges.at(i);
if (edge->Connects(node1, node2)) {
return edge->distance;
}
}
return -1; // should never happen
}
// Does the 'nodes' vector contain 'node'
bool Contains(vector<Node*>& nodes, Node* node) {
const int size = nodes.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
if (node == nodes.at(i)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
///////////////////
void PrintShortestRouteTo(Node* destination) {
Node* previous = destination;
cout << "Distance from start: "
<< destination->distanceFromStart << endl;
while (previous) {
cout << previous->id << " ";
previous = previous->previous;
}
cout << endl;
}
// these two not needed
vector<Edge*>* AdjacentEdges(vector<Edge*>& Edges, Node* node);
void RemoveEdge(vector<Edge*>& Edges, Edge* edge);
vector<Edge*>* AdjacentEdges(vector<Edge*>& edges, Node* node) {
vector<Edge*>* adjacentEdges = new vector<Edge*>();
const int size = edges.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
Edge* edge = edges.at(i);
if (edge->node1 == node) {
cout << "adjacent: " << edge->node2->id << endl;
adjacentEdges->push_back(edge);
} else if (edge->node2 == node) {
cout << "adjacent: " << edge->node1->id << endl;
adjacentEdges->push_back(edge);
}
}
return adjacentEdges;
}
void RemoveEdge(vector<Edge*>& edges, Edge* edge) {
vector<Edge*>::iterator it;
for (it = edges.begin(); it < edges.end(); ++it) {
if (*it == edge) {
edges.erase(it);
return;
}
}
}
Dijkstra's Algorithm Complexity
Time Complexity: O(E Log V)
where, E is the number of edges and V is the number of vertices.
Space Complexity: O(V)
Dijkstra's Algorithm Applications
- To find the shortest path
- In social networking applications
- In a telephone network
- To find the locations in the map