The Reader class of the java.io package is an abstract superclass that represents a stream of characters.
Since Reader is an abstract class, it is not useful by itself. However, its subclasses can be used to read data.
Subclasses of Reader
In order to use the functionality of Reader, we can use its subclasses. Some of them are:
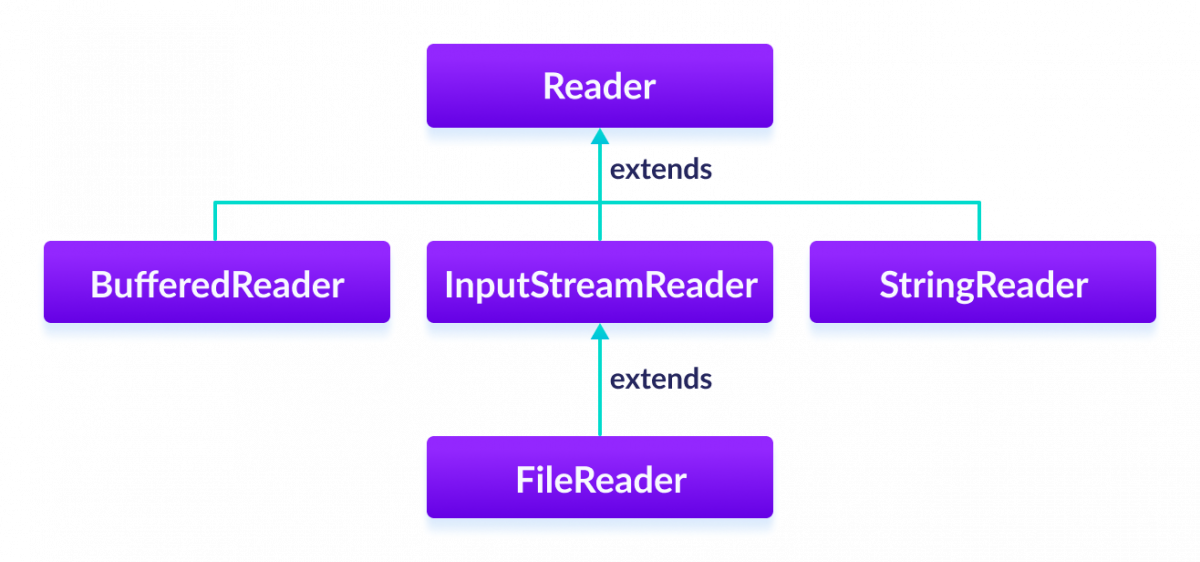
We will learn about all these subclasses in the next tutorial.
Create a Reader
In order to create a Reader, we must import the java.io.Reader package first. Once we import the package, here is how we can create the reader.
// Creates a Reader
Reader input = new FileReader();
Here, we have created a reader using the FileReader class. It is because Reader is an abstract class. Hence we cannot create an object of Reader.
Note: We can also create readers from other subclasses of Reader.
Methods of Reader
The Reader class provides different methods that are implemented by its subclasses. Here are some of the commonly used methods:
ready()- checks if the reader is ready to be readread(char[] array)- reads the characters from the stream and stores in the specified arrayread(char[] array, int start, int length)- reads the number of characters equal to length from the stream and stores in the specified array starting from the startmark()- marks the position in the stream up to which data has been readreset()- returns the control to the point in the stream where the mark is setskip()- discards the specified number of characters from the stream
Example: Reader Using FileReader
Here is how we can implement Reader using the FileReader class.
Suppose we have a file named input.txt with the following content.
This is a line of text inside the file.
Let's try to read this file using FileReader (a subclass of Reader).
import java.io.Reader;
import java.io.FileReader;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creates an array of character
char[] array = new char[100];
try {
// Creates a reader using the FileReader
Reader input = new FileReader("input.txt");
// Checks if reader is ready
System.out.println("Is there data in the stream? " + input.ready());
// Reads characters
input.read(array);
System.out.println("Data in the stream:");
System.out.println(array);
// Closes the reader
input.close();
}
catch(Exception e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
}
}
Output
Is there data in the stream? true Data in the stream: This is a line of text inside the file.
In the above example, we have created a reader using the FileReader class. The reader is linked with the file input.txt.
Reader input = new FileReader("input.txt");
To read data from the input.txt file, we have implemented these methods.
input.read(); // to read data from the reader
input.close(); // to close the reader
To learn more, visit Java Reader (official Java documentation).